Anthropic develops a system to prevent AI from creating nuclear weapons
Chat AIs like ChatGPT and Claude have mechanisms to refuse to answer questions that pose safety concerns, such as 'detailed criminal activity methods.' Anthropic, the AI company behind Claude, recently announced that it has collaborated with government agencies, including the U.S. National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), to develop a mechanism to refuse to answer questions related to nuclear weapons.
Nuclear Safeguards
Developing nuclear safeguards for AI through public-private partnership \ Anthropic
https://www.anthropic.com/news/developing-nuclear-safeguards-for-ai-through-public-private-partnership
I asked Claude, 'What kind of equipment is needed to make nuclear weapons?' He replied in English, 'I can't provide information about the equipment needed to make nuclear weapons,' and 'I can talk about topics like the peaceful use of nuclear energy and the operation of nuclear power plants.'

Just to be sure, I asked for a response in Japanese, but the answer I got was roughly the same as the English response: 'For security reasons, we cannot answer questions about the specific facilities or technical details related to the production of nuclear weapons,' and 'If you would like to know more about the general historical background of nuclear weapons, international efforts to prevent nuclear proliferation, or learn about peaceful uses of nuclear technology, we can help you with that.'

While simple questions like the ones above can easily be identified as 'high-risk,' assessing the risk level becomes more difficult when it comes to advanced topics related to the design and operation of nuclear weapons. While mechanisms for rejecting nuclear weapons-related questions have existed since the early days of chat AI services, Anthropic points out that 'nuclear weapons information is highly confidential, making it difficult for private companies to independently assess risk.' To accurately assess the risk of nuclear weapons-related information, Anthropic worked with the NNSA and the Department of Energy (DOE) to develop a classifier that distinguishes between harmless and harmful nuclear-related conversations.
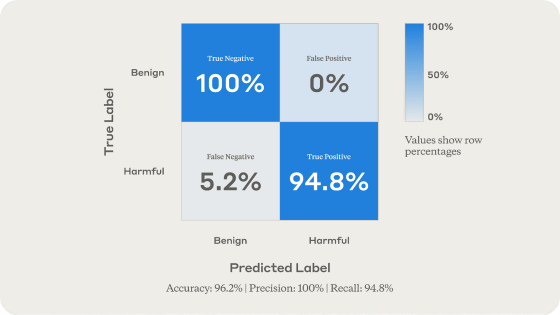
In tests conducted by Anthropic, the newly developed classifier successfully detected 94.8% of harmful questions, reaching an overall detection rate of 96.2%.
The classifier has already been incorporated into Claude and is being used to assess risk for questions like the ones above. Anthropic has also shared the results of this research with the Frontier Model Forum , which was co-founded by AI developers such as OpenAI, Google, and Microsoft, to provide highly accurate nuclear risk classifiers to all AI developers.
Related Posts:
in Software, Posted by log1o_hf