A study of eight AI search engines, including ChatGPT and Perplexity, found that more than 60% of search phrases provided incorrect citations of news articles, with Grok 3 being particularly bad, providing incorrect answers to 94% of search phrases.
In recent years, the popularity of AI-based search tools has rapidly increased, and many users are using AI search engines instead of traditional search engines to crawl the Internet and provide the latest relevant information. However, a survey of eight AI search engines, including
AI Search Has A Citation Problem - Columbia Journalism Review
https://www.cjr.org/tow_center/we-compared-eight-ai-search-engines-theyre-all-bad-at-citing-news.php

Traditional search engines generally act as intermediaries that guide users to news sites and other quality content. On the other hand, AI search engines automatically analyze and summarize information available on the Internet and provide it to users. Therefore, there is an urgent need to evaluate how AI search engines access, display, and cite news content.
For their experiment, the Tow Center for Digital Journalism randomly selected 10 articles from each news site, excerpted parts of those articles, and provided them as queries to each chatbot, asking them to identify the headline, source news site, publication date, and URL of the article that corresponded to the provided query.

Next, the responses from each chatbot were manually evaluated according to three attributes: 'Is the article headline correct?', 'Is the news site that distributed the article correct?', and 'Is the URL correctly obtained?'. The evaluation results were divided into six categories: 'Completely Correct' (all attributes are correct), 'Correct but Incomplete' (some attributes are correct but information is missing), 'Partially Incorrect' (some attributes are correct but other attributes are incorrect), 'Completely Incorrect' (all three attributes are incorrect or missing), 'No Answer Provided' (no information provided), and 'Crawler Blocked' (crawler blocked by
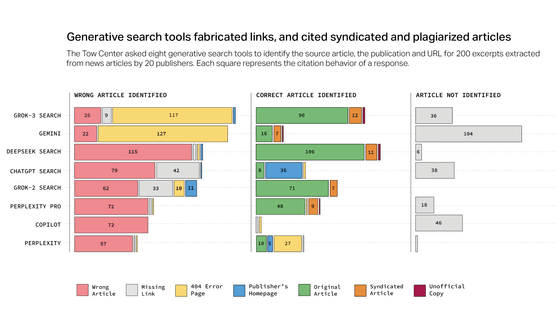
The results of the experiment, which covered ChatGPT search, Perplexity, Perplexity Pro, DeepSeek Search, Copilot, Grok 2, Grok 3, and Gemini, revealed that, overall, many of these AI search engines failed to retrieve the correct articles and provided incorrect answers for more than 60% of queries. The level of inaccuracy also varied across platforms, with Perplexity having an error rate of 37% and Grok 3 reaching an error rate of 94%.
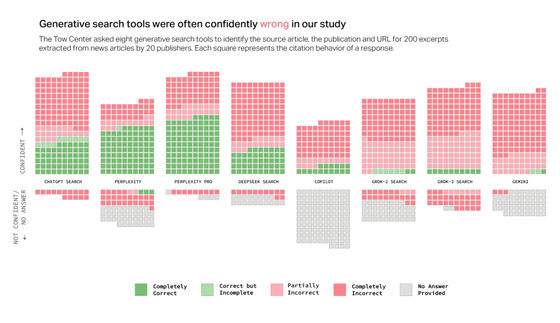
The Tow Center for Digital Journalism points out that 'Most of the tools we tested rarely used qualifying phrases such as 'may be' and confidently presented inaccurate answers. ChatGPT made errors in 134 answers out of 200 articles, but only 15 answers that included a phrase related to lack of confidence such as 'may be'.'
In addition, the Tow Center for Digital Journalism said that models that require payment to use, such as Perplexity Pro and Grok 3, had higher error rates. 'These results give users a potentially dangerous illusion of reliability and accuracy,' the Tow Center for Digital Journalism said.
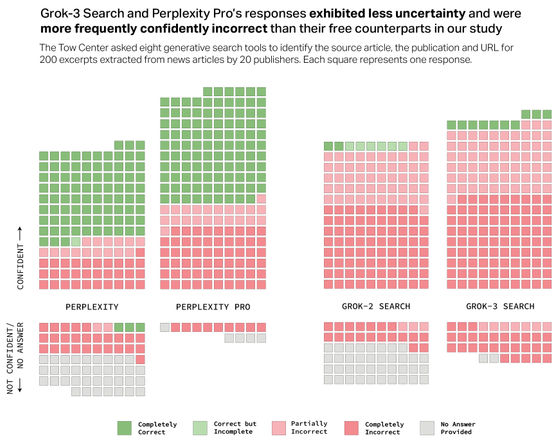
In addition, ChatGPT search, Perplexity, and Perplexity Pro
In response to the criticism that 'Perplexity's AI ignores robots.txt that blocks crawlers,' CEO claims that 'we don't ignore it, but we rely on third-party crawlers' - GIGAZINE

Additionally, these AI search engines have been reported to be prone to crediting incorrect sources. In particular, DeepSeek Search miscited sources 115 times out of 200 answers. The Tow Center for Digital Journalism said, 'Even when the chatbots appeared to correctly identify articles, they often did not properly link to the original sources.'
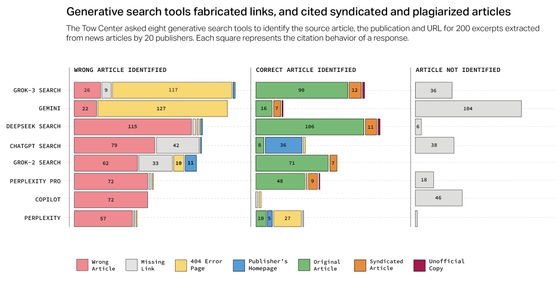
The Tow Center for Digital Journalism further reported that more than half of the responses from Gemini and Grok 3 presented fabricated or broken URLs, and despite OpenAI and Perplexity having partnership agreements with
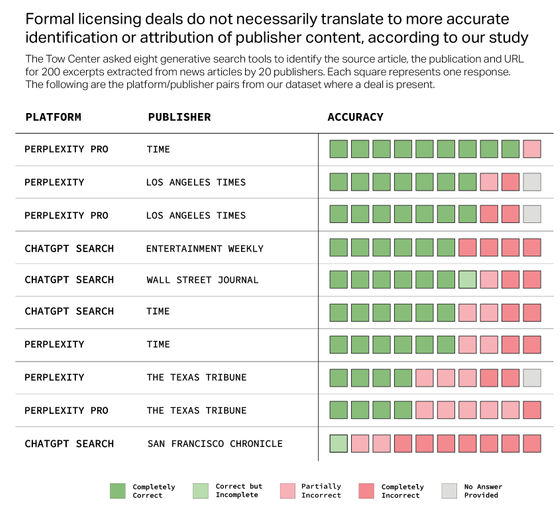
In response to the survey results, an OpenAI spokesperson said, 'We help 400 million ChatGPT users find quality content every week through summaries, citations, clear links, and attribution, and we support publishers and creators. We will continue to work with our partners to improve citation accuracy and enrich search results.' Microsoft also said, 'We comply with the robot.txt standards and will continue to respect instructions from websites that do not want content on their pages to be used in generative AI models.' Perplexity, DeepSeek, xAI, and Google have not commented.
Related Posts: