Wikipedia's traffic has fallen by 8% year-on-year due to the rise of AI. What can be done to save websites that are suffering from the spread of AI?
In the face of the proliferation of harmful social media and poorly written AI content, Wikipedia is sometimes called the '
New User Trends on Wikipedia – Diff
https://diff.wikimedia.org/2025/10/17/new-user-trends-on-wikipedia/
Wikipedia says traffic is falling due to AI search summaries and social video | TechCrunch
https://techcrunch.com/2025/10/18/wikipedia-says-traffic-is-falling-due-to-ai-search-summaries-and-social-video/
Marshall Miller, senior product director at the Wikimedia Foundation, which runs Wikipedia, posted a blog titled 'Wikipedia's Latest User Trends' on Diff , the Wikimedia Foundation's blog for volunteer communities.
The Wikimedia Foundation announced a ' Global Trends Impacting the Wikimedia Foundation ' in March 2025. These trends will continue to impact not only Wikimedia projects but the entire Internet. Miller points out that 'one of these trends is the increasing use of Wikipedia content by companies to support new AI experiences.'
In April 2025, the Wikimedia Foundation explained that 'bots and crawlers are placing excessive strain on the Wikimedia Foundation's infrastructure when searching Wikipedia content,' and that bots and crawlers continue to have a significant impact on Wikimedia project traffic data at the time of writing.
According to Miller, Wikipedia and other Wikimedia projects receive billions of page views from around the world every month. The Wikimedia Foundation uses algorithms to classify this traffic as human or bot-driven. This allows the Foundation to accurately identify human traffic and limit how third-party bots can obtain data to power commercial search and AI experiences. Many of the bots that scrape websites are becoming increasingly sophisticated and attempt to appear human. The Wikimedia Foundation is continually updating its traffic classification methods to keep its metrics as accurate as possible.
Around May 2025, an abnormal increase in human traffic originating from Brazil was detected. In response, the Wikimedia Foundation investigated and updated its bot detection system. It then reclassified traffic data from March to August 2025 using the new logic it developed. It was then revealed that the abnormal increase in traffic in May and June was due to bots designed to evade detection.
Analysis of historical traffic based on this bot detection logic revealed that human page views on Wikipedia have been declining over the past few months, down about 8% compared to the same period in 2024. The graph below summarizes human page views to Wikipedia in all languages by month since September 2021. Page views remained fairly constant until April 2025 (blue line), but have gradually decreased since April.
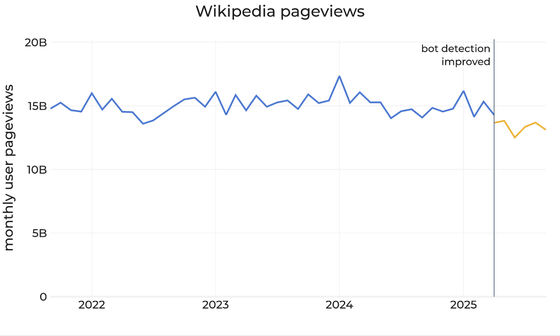
'We believe this decline in traffic reflects how generative AI and social media are influencing how people search for information, particularly as search engines increasingly provide answers directly to searchers based on Wikipedia content,' Miller said, suggesting that features like Google Search's ' AI-generated summaries ' are contributing to the decline in website traffic.
It has been reported that website traffic has dropped sharply since Google released its 'AI-powered summary' feature.
Reports that website traffic has plummeted due to 'AI summary' being displayed in Google search - GIGAZINE

Miller said the decline in traffic isn't unexpected, as search engines are increasingly leveraging generative AI to provide answers directly to searchers rather than linking to websites. It's also clear that younger generations are turning to social video platforms for information rather than the open web, which means less usage of websites like Wikipedia.
These shifts in user behavior are not unique to Wikipedia: Many publishers and content platforms report similar shifts as users spend more time looking for information in search engines, AI chatbots, and social media. And it's clear that AI is putting a strain on the infrastructure of websites like Wikipedia.
Wikimedia Foundation announces that 'relentless AI scraping is straining infrastructure' - GIGAZINE
Miller said, 'These trends mean that some users are no longer directly accessing Wikipedia for information, but Wikipedia remains one of the most valuable datasets on which new forms of knowledge dissemination rely. Nearly all large-scale language models (LLMs) are trained on Wikipedia, and search engines and social media platforms prioritize Wikipedia information to answer user questions. This means that even if you don't visit Wikipedia, Wikimedia knowledge is being read across the Internet. Human-created knowledge (Wikipedia) is becoming even more important for the dissemination of reliable information online. And indeed, Wikipedia continues to be highly trusted and valued around the world as a neutral and accurate source of information, as measured by large-scale surveys regularly conducted by the Wikimedia Foundation.'
While the Wikimedia Foundation welcomes new ways for people to access knowledge, it also points out that LLMs, AI chatbots, search engines, and social platforms that use Wikipedia content must encourage more visitors to Wikipedia to ensure the continued flow of free knowledge on which so many people and platforms rely. Fewer visitors to Wikipedia could mean fewer volunteers to enrich its content and fewer individual donors to support this work.
'Wikipedia is the only major source of information on the internet with standards of verifiability, neutrality, and transparency, and it remains an invisibly essential part of people's daily information needs,' Miller said. 'For people to trust the information shared online, platforms need to clarify the origins of information and increase opportunities to access and participate in those sources.'
While the latest traffic trends and other data point to changes in how users and content are used, Miller argues that there are many steps that can be taken to ensure the long-term sustainability of Wikimedia content. 'First, everyone can choose to take online actions that support content integrity and content creation,' Miller said. Specifically, when searching for information online, Miller emphasizes checking citations and clicking links to the original source. He also said, 'Talk to those close to you about the importance of knowledge curated by trusted humans. Help them understand that the content that generative AI relies on is created by real people who deserve their support.'

Furthermore, active volunteers can 'go further in this important phase by working with the Wikimedia Foundation team to test new Wikipedia experiences and tools. As the internet changes rapidly, now is the time to consider which parts of Wikipedia should change and which parts should stay the same while keeping our promise to provide the world with free, human-centered knowledge.'
'Twenty-five years after its founding, the knowledge of humanity that Wikipedia holds is more valuable to the world than ever before. Our vision is a future in which everyone can participate in creating and sharing knowledge, and we can achieve this by everyone using this free knowledge ecosystem responsibly. We ask everyone to support our knowledge platform in both old and new ways, and we are confident that Wikipedia will continue to exist and that the Internet will continue to provide free and accurate knowledge of humanity for future generations,' said Miller.
Related Posts:
in Web Service, Posted by logu_ii