'Animated AI' provides an animated explanation of convolutional neural network processing
A website called 'Animated AI' has been published that uses animation to explain 'Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN),' a technology widely used in the field of machine learning. The website visually explains how the network works, which is difficult to understand through text alone.
Animated AI
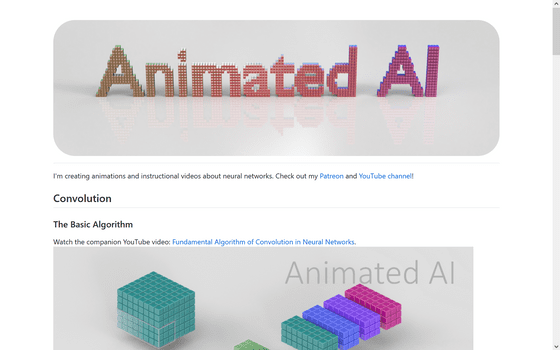
Convolutional neural networks are a technique that applies weighting to input data such as images through filters, making it easier to recognize the shape of the data. For more details, see the following article.
An easy-to-understand explanation of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) from the basics to implementation – Experiential learning blog by zero to one
Animated AI displays animated gifs on topics such as the basic operation of convolution processing, a process called 'padding' that corrects for the problem of the output data size being reduced by convolution processing, and the 'stride' of the filter movement interval, and also includes links to YouTube videos that explain each topic.
For example, here's an animation showing the basics: Click on the image to play it.
Here's a YouTube video that explains the basics:
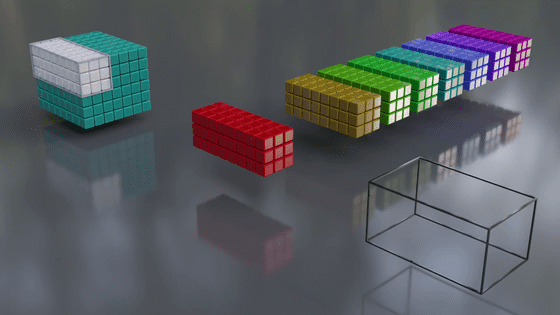
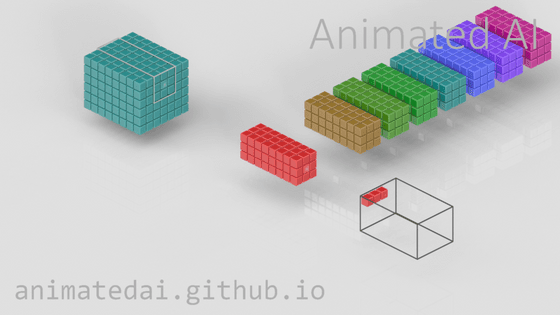
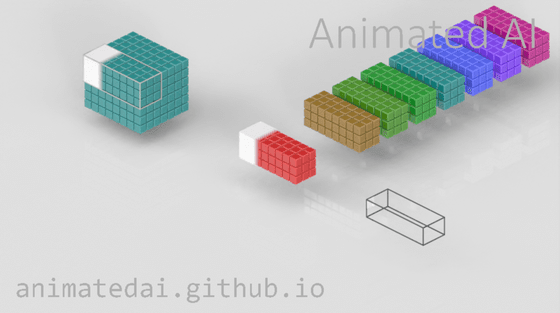
The cube in the back is the input data. The data is divided into a grid, and the characteristics of each point (pixel) are quantified.
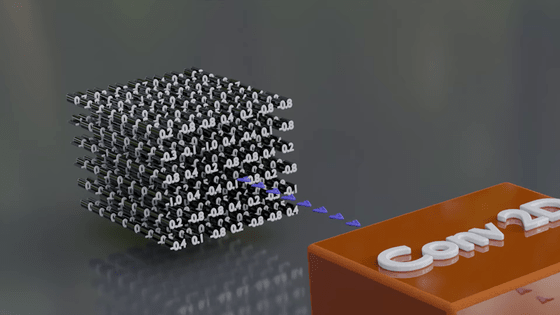
The cubes in the foreground are filters. They extract a portion of the input data (for example, a 3x3 area), and weight it by multiplying the input data by the number assigned to each filter. By weighting, it becomes easier to recognize the numerous features of each pixel, such as color and shape.
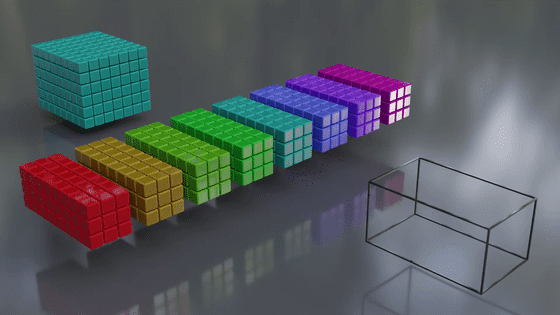
A specific range is filtered, and when one range is finished, it moves to the next square and filters the next range... and repeats this process until all ranges are processed. The interval between range movements is the stride.
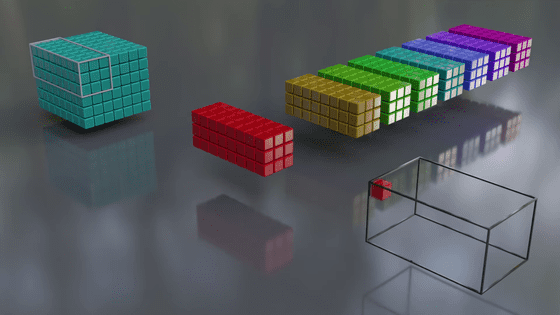
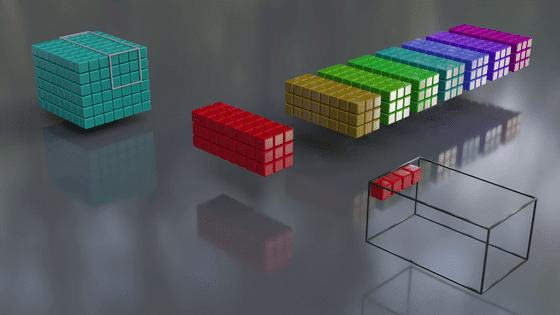
Once processing is complete with one filter, it is processed again with the next filter, and this process is repeated.
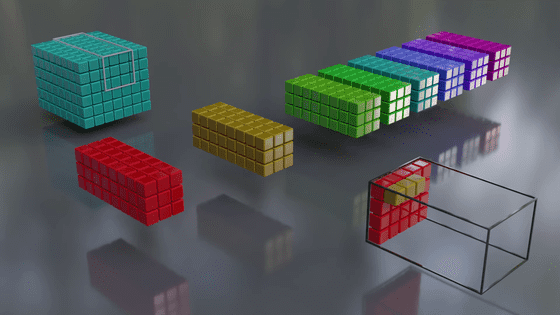
When processing data, the output data will be smaller than the original data. To prevent this, pixels with values such as '0' are added around the original data to adjust the size. This is a technique called 'padding.'
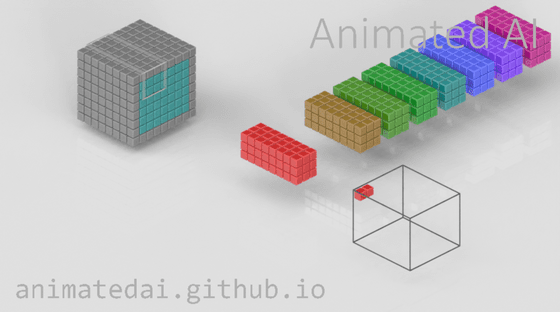
Shifting the filter range by one square is stride 1, and shifting it by two squares is stride 2. This is animated in the video below.
In addition, techniques called 'depthwise separable convolution' and 'pixel shuffling' are also explained.
Related Posts: