A large-capacity cassette tape system that can store data for a long period using DNA will be developed, theoretically capable of storing 362 petabytes per km
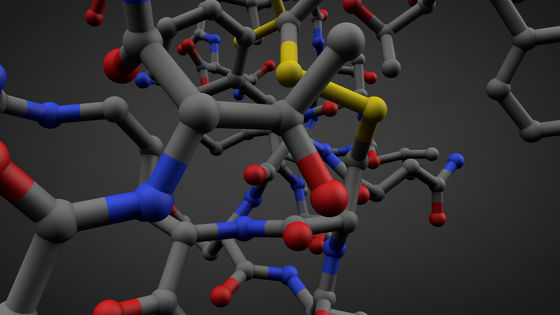
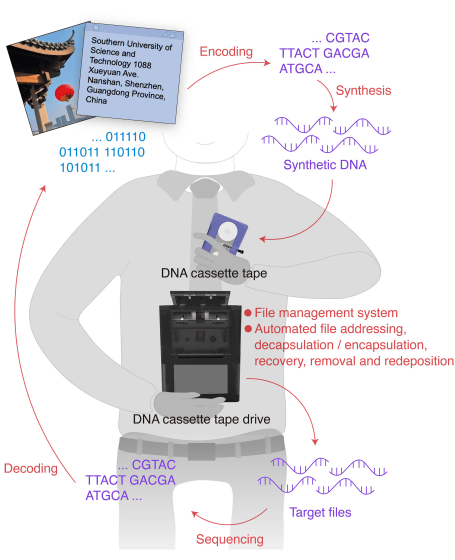
DNA stores genetic information in the order of four bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Research is underway to utilize DNA's information storage capacity to store electronic data such as text and images. A research team at the Southern University of Science and Technology in China has developed a cassette tape-type device that can store data using DNA. Theoretically, 1 km of tape can store up to 362 petabytes (362,000 terabytes) of data.
A compact cassette tape for DNA-based data storage | Science Advances
Modern computers represent data as a string of two values: '1' and '0.' DNA, on the other hand, uses four values: 'A,' 'T,' 'G,' and 'C,' allowing it to store data at a higher density than existing data representation formats. DNA also has the advantage of being able to store data for long periods of time, as evidenced by the fact that DNA from organisms over a million years ago has been preserved to the present day.
The research team devised a method to convert the data into a sequence of 'A', 'T', 'G', and 'C', and then arrange the DNA constructed according to that sequence on the tape. Using this method, it is theoretically possible to store 362 petabytes of data per kilometer. However, because space is required for 'barcodes to record the position information of each DNA' and to ensure error tolerance due to DNA loss, the realistic storage capacity is estimated to be around 74.7 gigabytes per kilometer.
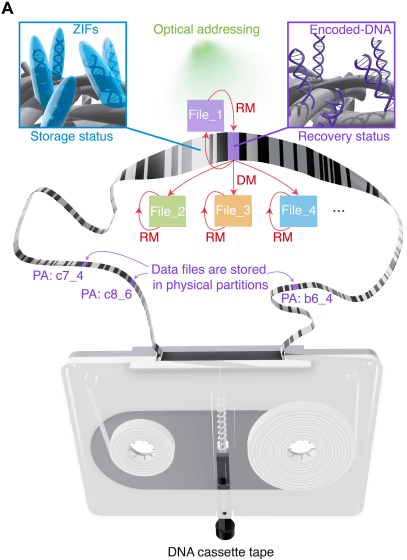
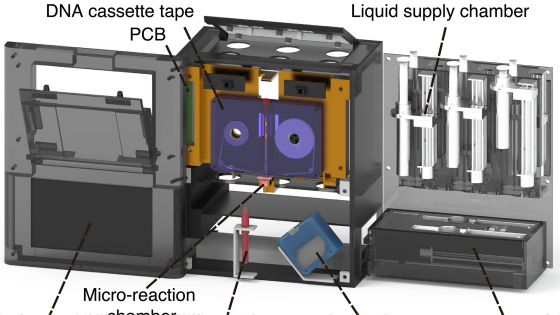
The data is read using a device shaped like a cassette tape recorder, which contains a barcode reader, optical sensors, and various solutions.
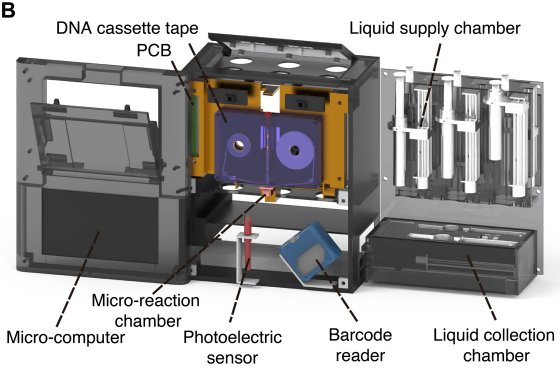
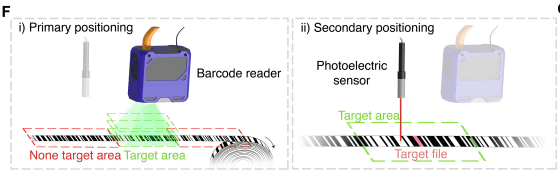
When reading the data, a barcode reader is first used to find the 'area where the target DNA is located,' and then an optical sensor is used to read the DNA sequence.
The cassette tape and reading device are hand-held size.
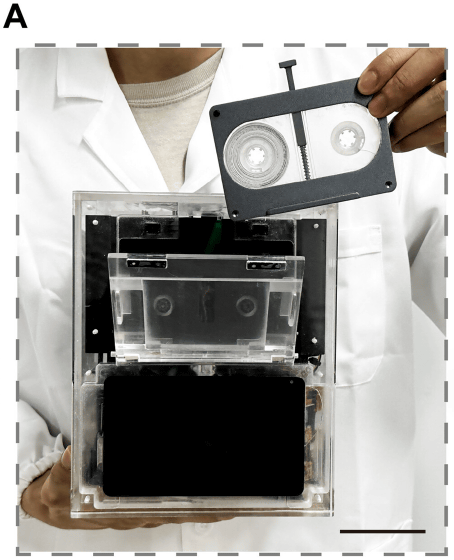

The DNA cassette tape is currently in an experimental stage, and it takes 150 minutes to restore three image files and rearrange one image file. In the future, it is expected that a small storage system capable of storing large amounts of data will be realized.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1o_hf