What's new in the core specifications of Bluetooth 6.2? The ultra-short connection interval significantly improves devices that require ultra-low latency, such as gaming keyboards and pen tablets.

Core Specification | Bluetooth® Technology Website
https://www.bluetooth.com/specifications/specs/core-specification-6-2/
Bluetooth® Core 6.2 feature overview | Bluetooth® Technology Website
https://www.bluetooth.com/bluetooth-core-6-2-feature-overview/
What's new in Bluetooth®︎ Core 6.2: An overview - Blogs - Nordic Blog - Nordic DevZone
https://devzone.nordicsemi.com/nordic/nordic-blog/b/blog/posts/whats-new-in-bluetooth-core-6-2-an-overview
Bluetooth 6.2 gets more responsive, improves security, USB communication, and testing capabilities - CNX Software
https://www.cnx-software.com/2025/11/05/bluetooth-6-2-gets-more-responsive-improves-security-usb-communication-and-testing-capabilities/
The most notable specification of Bluetooth Core 6.2 is the reduction of the minimum connection interval from 7.5 milliseconds in Bluetooth LE to 0.375 milliseconds (375 microseconds). This is made possible by a technology called 'Bluetooth Shorter Connection Intervals (Bluetooth SCI),' which enables ultra-low latency connections with polling rates exceeding 2 kHz in secure connections. Nordic DevZone, a developer community that contributed to the development of Bluetooth SCI, described this as 'a feature that many Bluetooth developers and users have been waiting for.'
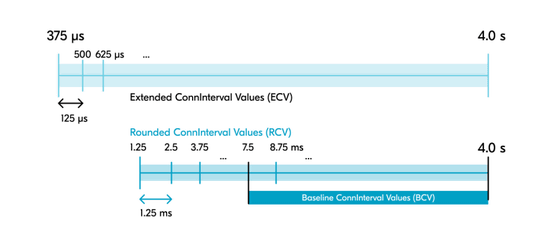
Bluetooth SCI has two important improvements over Bluetooth LE. One of them is that it 'sets the lower limit of the connection interval in the Bluetooth Core specification to be shorter than 7.5 milliseconds.' Bluetooth SCI extends the range of connection intervals from 375 microseconds to 4.0 seconds, with a resolution defined as a multiple of 125 microseconds. This range is called Extended ConnInterval Values (ECV).
Additionally, two subset ranges, 'RCV' and 'BCV', are defined. RCV is defined as all values where the ECV resolution is a multiple of 1250 microseconds, and BCV is defined as all values where the RCV resolution is 7.5 milliseconds or greater. The following diagram more clearly illustrates these different ranges. You can see that BCV corresponds to the same range of connection intervals defined in Bluetooth Core 6.2 and earlier.
If a Bluetooth-enabled controller supports Bluetooth SCI, it must support all values of RCV (1.25 ms to 4.0 s, in 1.25 ms increments). It may also optionally support other values of ECV. The supported values must be specified by the controller. If it does not support Bluetooth SCI, the controller must support all values of BCV, but is not required to support other values.
Controllers that support Bluetooth SCI must also support the Connection Subrating feature. Furthermore, to fully utilize Bluetooth SCI, they must also support Frame Space Update (FSU). FSU optimizes the interval between adjacent transmissions, T_IFS, and can be negotiated to a value less than 150 microseconds in Bluetooth Core 6.0 and later.
When establishing a new connection, the default connection interval must be within the BCV range. The connection interval can then be updated to the ECV range, i.e., a shorter connection interval, by using a newly defined connection rate update procedure on the central side or a connection rate request procedure on the peripheral side. The central side can reject the connection rate request procedure.
Additionally, 'LE Flushing ACL Data' allows data packets marked as flushable by the host to be dropped if the packet in the transmit queue is older than the specified flush timeout. Taking a human interface device (HID) mouse as an example, LE Flushing ACL Data Packets is useful when input data from the mouse is being retransmitted due to interference, but after a certain period of time, some of the next data in the transmit queue becomes irrelevant and invalid. Marking data as flushable improves mouse responsiveness by eliminating the need to transmit old data packets. Note that packets that have been sent but not yet acknowledged cannot be flushed because they must be retransmitted until acknowledged. Only packets that exceed the flush timeout before their first transmission opportunity can be flushed.

For products requiring ultra-low latency, such as gaming mice, gaming keyboards, pen tablets, and stylus pens, shortening the connection interval and flushing HCI ACL data are important. Until now, the polling rate of Bluetooth LE gaming accessories has generally been limited to around 125 Hz, which is not sufficient for all gamers. However, by utilizing Bluetooth SCI, the polling rate can theoretically be increased to 2 kHz or higher. However, HID devices that support Bluetooth SCI require some overhead for reporting and Bluetooth stack processing, so in practice they can only provide a polling rate of 1 kHz to 2 kHz. Still, significant improvements in connection intervals are expected to bring a major leap forward for gaming mice, gaming keyboards, pen tablets, and stylus pens.
Bluetooth Core 6.2 also includes enhanced protection against advanced amplitude-based RF attacks, making devices for the automotive, smart home and industrial markets less susceptible to relay attacks and spoofing threats.
Additionally, Bluetooth HCI USB LE Isochronous Support adds bulk serialization mode, a new mechanism for standardizing isochronous data transfer over USB. This update simplifies packet processing in the Host Controller Interface (HCI) and also streamlines the integration of LE Audio in Bluetooth USB devices.
Additionally, Bluetooth LE test mode enhancements enable a unified control protocol for performing Bluetooth LE RF PHY tests, and also support over-the-air (OTA) transport, eliminating tester reliance on cables.
Related Posts:
in Software, Posted by logu_ii