Microsoft researchers report 'Whisper Leak' attack that identifies conversations with AI chatbots from communication packets and transmission timing
Researchers at Microsoft have reported a vulnerability called 'Whisper Leak' in large-scale language models ( LLMs ) that power AI chatbots such as ChatGPT and Google Gemini, which allows for the topic of conversation to be inferred even from encrypted communications. The vulnerability was confirmed to affect many of the 28 LLMs tested.
[2511.03675] Whisper Leak: a side-channel attack on Large Language Models
Microsoft finds security flaw in AI chatbots that could expose conversation topics
https://techxplore.com/news/2025-11-microsoft-flaw-ai-chatbots-expose.html
Chat information with AI assistants is usually protected by TLS (Transport Layer Security), the same encryption technology used for online banking, which hides the contents of communications from eavesdroppers.
However, the Whisper Leak attack does not break this encryption, but rather exploits the 'metadata' that TLS encryption cannot hide. Specifically, when LLM generates responses, it uses a technique called 'streaming' to send generated tokens immediately or in small batches to improve the user experience.
The TLS encryption method has the property that the size of the communication content is roughly proportional to the encrypted packet size. Therefore, even with encrypted traffic, the pattern of the series of 'packet size' and 'transmission timing' sent can be observed by an attacker monitoring the network. Whisper Leak analyzes this leaked metadata pattern.
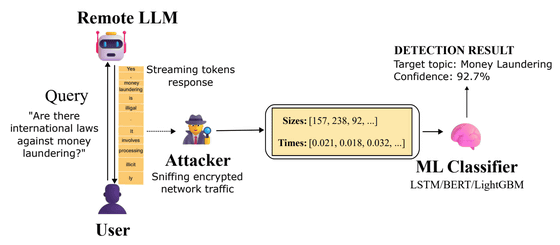
To demonstrate this vulnerability, the researchers first created two sets of questions: one set of 100 differently phrased questions on the specific topic of 'the legality of money laundering,' and the other set of 11,716 random, everyday queries extracted from a dataset on the Q&A site Quora. They then sent these to a major LLM and recorded the encrypted network traffic. Using only the collected metadata, they then trained LightGBM-, LSTM-, and BERT-based machine learning classifiers to identify whether the conversations were about the specific topic.
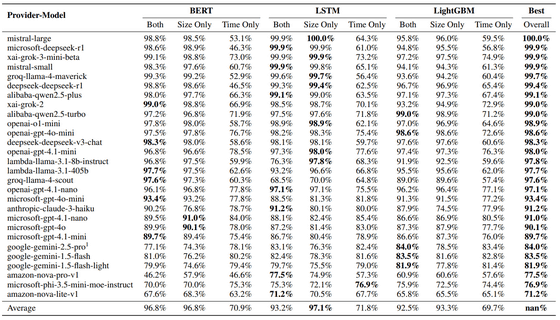
As a result of the experiment, the success rate of the attack was extremely high, exceeding 98%, for 17 of the 28 AI models investigated, so the research team argues that Whisper Leak is a very effective attack method.
The table below summarizes the effectiveness of Whisper Leak against 28 different models. 'BERT,' 'LSTM,' and 'LightGBM' are machine learning models used by attackers to infer conversation content. They identify conversation content using three methods: Size Only (packet size information only), Time Only (time interval only), and Both. Many of the top-ranked models (17 models) achieved very high scores (AUPRC) exceeding 98% against multiple attack methods. On the other hand, some models, such as Google Gemini and Amazon Nova, tend to score lower than other models, suggesting they are relatively resistant to Whisper Leak.
To simulate a more realistic scenario, the research team simulated a scenario in which '10,000 everyday conversations contain just one conversation about a specific topic.' As a result, it was found that in 17 out of 28 models, attackers could identify specific conversations that actually occurred in 5% to 20% of the conversations. In other words, Whisper Leak attackers could pinpoint users who were talking about a specific topic.
The research team warned, 'Whisper Leak could be carried out by passive attackers who can monitor encrypted traffic, such as internet service providers, government agencies, or even local network monitors like cafe Wi-Fi.' 'The industry needs to ensure the security of future systems. Our findings highlight the need for LLM providers to address metadata leaks as AI systems handle increasingly sensitive information.'
Related Posts: