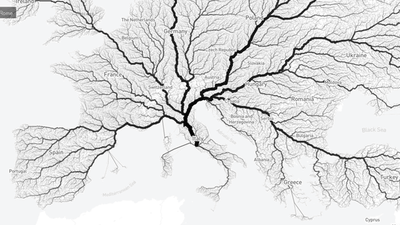
A new dataset of Roman roads has been created, increasing the total length of mapped roads by more than 100,000 km

As the saying goes, '
Itiner-e: A high-resolution dataset of roads of the Roman Empire | Scientific Data
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41597-025-06140-z

Massive New Map Reveals 300,000 Km of Ancient Roman Roads : ScienceAlert
https://www.sciencealert.com/massive-new-map-reveals-300000-km-of-ancient-roman-roads
Roman road network was twice as large as previously thought, new mapping project finds | Live Science
https://www.livescience.com/archaeology/romans/roman-road-network-was-twice-as-large-as-previously-thought-new-mapping-project-finds
At its peak, the Roman Empire controlled a territory of 5 million square kilometers, and its influence continues to this day in various fields, including culture, art, and architecture. The Roman Empire is also known for building roads throughout its territory, and this network of roads is said to have played a major role in maintaining and prospering the empire.
'Understanding how roads were laid out within the territory is important for understanding how Romans traveled and traded with each other, how the empire's scope changed over time, and the routes by which diseases spread. However, the data available on the Roman Empire's road network until now has been old and fragmented.'
Therefore, a research team led by Associate Professor Tom Brugmans, an archaeologist at Aarhus University in Denmark, launched the 'Itiner-e' project to consolidate fragmented data on Roman roads in one place and make that information available to everyone.

The research team used
'We compared evidence from excavations and documents with satellite imagery to identify traces of ancient roads and historical topography that points to a pre-urban era when Roman roads may have been more prominent than they are today,' said Brugmans. 'Using historical satellite imagery taken before the proposed dam construction even allowed us to find roads hidden beneath the current reservoir.'
As a result of this work, a dataset spanning 40 modern-day countries was created, increasing the total length of known Roman roads from 188,554 km in DARMC to 299,171 km. 'That's more than seven times the circumference of the Earth,' said Burgmans. 'This period saw a fundamental restructuring of the region's transportation infrastructure on a scale not seen until the Industrial Revolution in the 19th century. Now we have a dataset that allows us to study how land mobility changed over the course of 2,000 years.'
The research team's 'Itiner-e' can be accessed from the following website:
itiner-e
https://itiner-e.org/
Once you visit, you can see the Roman roads that were discovered through research.
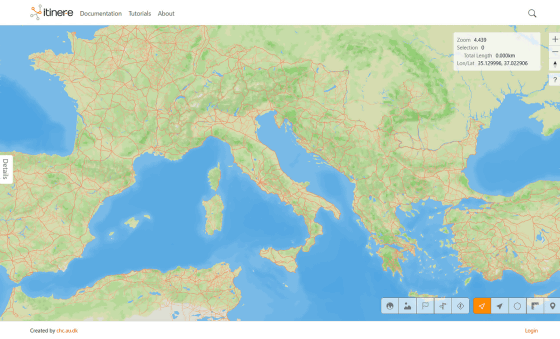
The road near the Strait of Gibraltar, which separates Europe and Africa, looks like this. You can see that the road is stretched all the way to the edge of the continent.
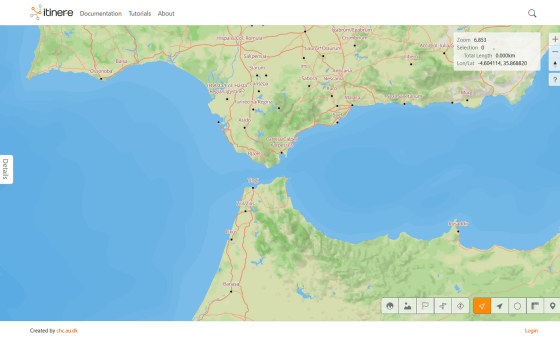
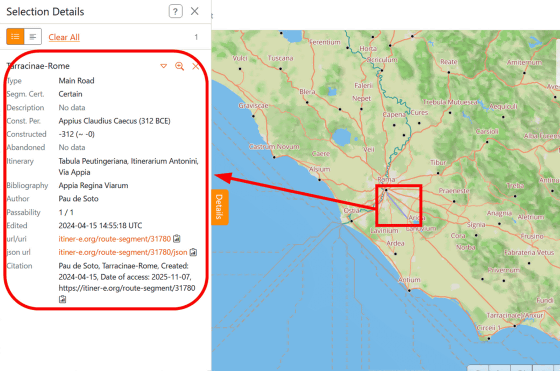
Users can also click on roads on the map to view more information about them and their data sources. 'The main contribution of this project is that it brings together all the research on Roman road locations in an open and accountable way,' said Brugmans. 'Each of the 14,769 road segments includes the source of information used to determine its location and an indication of the certainty of its location.'
Although the distance of Roman roads identified by Itiner-e is enormous, it is estimated to only account for about 3% of the entire road network during the Roman Empire. 'This was a great surprise and a sobering thought,' said Burgmans. '300,000 km is just the tip of the iceberg. We hope to encourage further research to further enrich the public information on the locations of Roman roads.'
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1h_ik