What is the 'Brain Rot' hypothesis that AI becomes stupid by learning garbage-like data?

The mass posting of low-quality content on social media that can be enjoyed without using one's brain is commonly referred to as 'brain rot content.' This term is used to criticize people who are addicted to social media, implying that endless viewing of short videos and insignificant images will rot the brain. However, it has become clear that AI, like humans, may also exhibit phenomena that warrant the term 'brain rot.'
LLMs Can Get 'Brain Rot'!
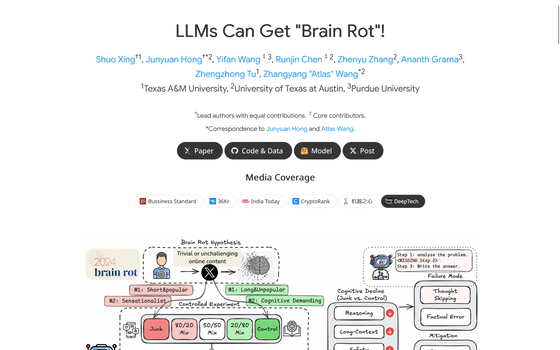
Shuo Xin and others at Texas A&M University have proposed the 'brain rot' hypothesis, which states that the performance of large-scale language models (LLMs) deteriorates when they are continuously trained on garbage data.
Shin and his colleagues conducted an experiment to determine whether low-quality content could impair LLM's function, just as low-quality content can impair human cognitive function.

First, Shin and his colleagues collected several posts from X (formerly Twitter) and classified each as either 'junk' or 'control.'
For example, content with many likes, reposts, and replies (especially very short posts) was classified as junk, as it attracts attention but contains shallow information, while long posts with low spreading power were used as the control group. We also looked at whether the text was sensational, contained clickbait-like expressions ('WOW,' 'LOOK,' 'TODAY ONLY'), or made exaggerated claims, and classified posts that contained an abundance of these as junk, while fact-based, educational, or logical posts were used as the control group.
Next, Shin and his colleagues continuously trained the collected data on four LLMs and conducted benchmark tests measuring cognitive function, reasoning ability, memory, and multitasking. They found that training on junk training significantly reduced performance in areas such as reasoning ability, long-form comprehension, and safety, and increased indicators of 'dark personality traits' that reflect psychopathic and narcissistic traits.
In particular, LLMs affected by junk data were found to fail inference more often and to gradually shorten or skip inference chains.

'The cognitive decline that accompanies brain decay cannot be easily mitigated by existing fine-tuning techniques,' Shin and his colleagues wrote. 'We found that even if the LLM is trained with high-quality data later, the effects of the junk data introduced initially remain for a long time.'
'These results suggest a need for a rethinking of current practices of internet data collection and continuous pre-training,' Singh et al. added. 'As LLMs become more widely used and incorporate larger datasets, careful curation and quality control will be essential to prevent cumulative harm.'
Related Posts:
in AI, Posted by log1p_kr