What happens to the brain when you use the drug 'amphetamine' to boost your concentration?

The Drug That Works TOO Well? - YouTube
Amphetamines are drugs that can get you through a tough work shift, push you through boring schoolwork, or give you the strength to dance until the crack of dawn.

During World War II, it was used by soldiers in various countries, including Japan, to increase their alertness, and it is also used as a drug to treat ADHD in children.

Over the past 15 years, amphetamines have become one of the fastest-growing drug markets in the world, second only to cannabis.

Like any other drug, amphetamines can be used to 'escape reality.'

But what sets amphetamines apart from other drugs is that they can also help people navigate modern society.

Nearly every human activity relies on focus and motivation. Whether you're working, playing, studying, creating, exercising, partying, or competing, you need to overcome fatigue, suppress distractions, and maintain focus.

Amphetamines are stimulants, and they support this very well. The three most common stimulants are amphetamines (such as speed and prescription drugs like Adderall and Vyvanse), methamphetamines (more powerful and highly addictive), and MDMA (those with special effects like ecstasy).
The main effect of amphetamines is to trick the brain into releasing large amounts of
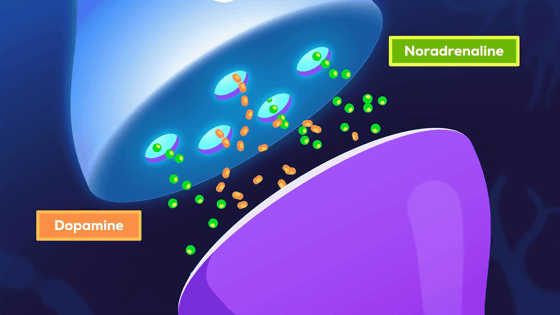
Dopamine is a chemical that promotes motivation and excitement, similar to the euphoria you get when you think, for example, 'Maybe I'll beat the final boss in a game.'

Norepinephrine is the chemical responsible for alertness, focus, and alertness, giving you the power to move your fingers quickly and accurately and pull off killer combos. Dopamine tells you 'this is important!', and norepinephrine gives you the 'power to see it through.'

Amphetamines increase concentration, make boring tasks more enjoyable, make people less distracted, increase heart rate, quicken breathing, and eliminate appetite and fatigue.

While other stimulants, such as cocaine, have a rapid onset of effect followed by a quick rebound, amphetamines can have effects that last from 4 to 14 hours.

Amphetamines were once widely prescribed for weight loss, depression, and nasal congestion.

However, at the time of writing, it is primarily used as a treatment for

The ADHD brain has difficulty concentrating because it cannot obtain rewards, and amphetamines help compensate for this.

As ADHD diagnoses have risen, so has the amount of amphetamines prescribed.
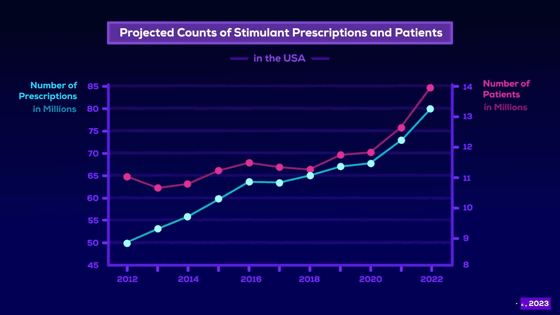
But amphetamines are also widely used as performance-enhancing tools, Kurzgesagt said. Amphetamine use is widespread in busy, competitive jobs, from technology and finance to chefs, truck drivers, surgeons, and nurses.

More than 4 million people in the United States alone illegally use prescription stimulants, especially college students who take amphetamines to 'improve their grades.'

But behind the bright side there is also a dark side.
For example, you may become absorbed in playing games instead of working, an excess of norepinephrine may cause anxiety, tension, and panic, you may become irritated by the slowness of others' speech and your relationships may deteriorate, you may forget to eat, sleep, and drink enough water and end up in poor health, or you may stay awake for long periods of time and not be able to fall asleep, causing fatigue to carry over to the next day.

The post-dose 'rebound' is also severe, with dopamine levels plummeting, leaving you feeling extremely tired, depressed, and anxious.

Constantly taking in artificial dopamine disrupts your emotional threshold, making it harder to experience pleasure, building tolerance, and requiring more dopamine.

Additionally, long-term use of amphetamines increases the risk of psychosis (which can lead to hallucinations, delusions, and schizophrenia) and cardiovascular damage (blood vessel damage, cardiac arrest, arrhythmia, stroke, etc.).
While short-term, low-dose medical use is considered relatively safe, long-term, high doses by healthy individuals are extremely dangerous.
While amphetamines are effective drugs for treating illnesses, they can certainly have adverse health effects if used improperly. Therefore, 'they are both fuel for society's rapid revolution and a health risk,' Kurzgesagt points out. 'They may be helpful in the short term, but they are not a sustainable solution in the long term,' he concludes.

Related Posts: