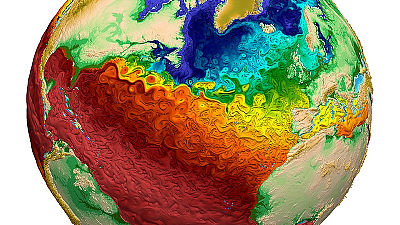
Research results show that the improvement of air pollution in East Asian countries such as China has accelerated global warming

Global warming has
East Asian aerosol cleanup has likely contributed to the recent acceleration in global warming | Communications Earth & Environment
https://www.nature.com/articles/s43247-025-02527-3
Cleaner air in east Asia may have driven recent acceleration in global warming, our new study indicates
https://theconversation.com/cleaner-air-in-east-asia-may-have-driven-recent-acceleration-in-global-warming-our-new-study-indicates-260601
Since the Industrial Revolution in the mid-18th century, humans have used fossil fuels in large quantities, and in the process, emissions of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide have increased. As a result, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has risen from 280 ppm before the Industrial Revolution to about 420 ppm at the time of writing , which is the cause of global warming.
However, global warming has been progressing faster since 2010 compared to before, and climate scientists have not been able to fully understand why. Previous studies have reported that the reduction in sulfur emissions from the shipping industry, which has implemented measures to combat air pollution, may have accelerated global warming. This is because aerosols, which are made up of air pollutants such as sulfur dioxide , also have the effect of blocking sunlight and increasing the reflectivity of clouds.
Ironically, the reduction in ocean air pollution may have 'accelerated global warming' - GIGAZINE

However, the tightening of regulations on sulfur emissions from the shipping industry only began in 2020 and is insufficient to explain the acceleration of global warming between 2010 and 2020. An international research team led by Bjorn Samset , a senior researcher at the Norwegian Center for International Climate and Environmental Research , hypothesized that 'improvements in air pollution in East Asian countries, especially China, may be related to the acceleration of global warming.'
In recent years, China has succeeded in improving air pollution through strict environmental measures, with fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in Beijing reportedly decreasing by 66.5%, nitrogen dioxide by 58.9%, and sulfur dioxide by 88.7% in the 10 years since 2013. Samset and his colleagues point out that sulfur dioxide emissions in East Asia as a whole have also decreased by 75% since 2013, which coincides with a period of accelerated global warming.
The researchers ran 160 computer simulations using eight climate models developed by teams around the world to quantify the impact of reduced air pollution in East Asia on global temperature and precipitation patterns, and analyse links to global warming.
The analysis found that improvements in air pollution in East Asia have led to an extra 0.07°C of global warming. This seems small compared to the roughly 1.3°C warming since 1850, but it is enough to explain the acceleration of global warming since 2010, once year-to-year variations due to events such as El Niño , which affect global weather patterns, are removed.
Based on historical long-term trends, a warming of about 0.23°C was predicted since 2010, but the actual warming reached about 0.33°C. This extra 0.1°C can be largely explained by improved air pollution in East Asia, along with other factors such as stricter sulfur regulations in the shipping industry.

'Air pollution has a cooling effect, either by reflecting sunlight itself or by changing the properties of clouds so that they reflect more sunlight,' said Samset and his colleagues. 'Improved air pollution in East Asia will affect global temperatures by reducing the shading effect of air pollution in East Asia. It will also reduce the amount of sunlight reflected by clouds in the eastern Pacific Ocean by reducing the amount of pollutants crossing the North Pacific.'
The pattern of change in the North Pacific simulated in this study is consistent with the pattern observed by satellite. It is also believed that the relatively strong warming occurring in the North Pacific, which is downwind from East Asia, is due to the improvement in air pollution in East Asia.
Some people may think, 'If improving air pollution accelerates global warming, then surely it's better to leave air pollution as it is?' However, air pollution is said to be the most serious health risk to humans, and improving air pollution is important for improving human health and life expectancy.
The biggest threat to human health is not the virus, what is shortening human lifespan the most? - GIGAZINE

'Greenhouse gas emissions remain the primary cause of global warming, and the reduction in air pollution was necessary. The reduction in air pollution did not cause further warming, but rather removed the artificial cooling effect that temporarily protected us from extreme weather and other impacts of climate change. Global warming will continue for decades to come. Our past and future greenhouse gas emissions will affect the climate for centuries. However, because air pollution is quickly lost from the atmosphere, the acceleration of global warming due to the loss of cooling effect is likely to be temporary,' Samset and his colleagues wrote.
Related Posts:
in Free Member, Science, Posted by log1h_ik