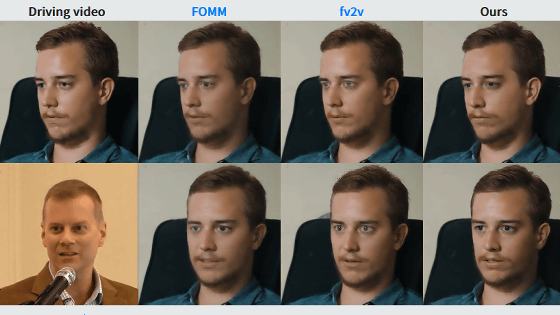
A method called 'real-time chunking (RTC)' will be developed to give AI robots the ability to respond to 'real-time changes in the real world', enabling precise movements such as lighting a match or folding clothes

Research is underway on AI-equipped robots that can perform tasks while recognizing the state of the real world, but AI-equipped robots have the challenge of 'responding to real-time changes in the real world.' A new algorithm that can respond to real-time changes, called 'real-time chunking (RTC),' has been developed by a research team at the University of California, Berkeley.
Real-Time Action Chunking with Large Models
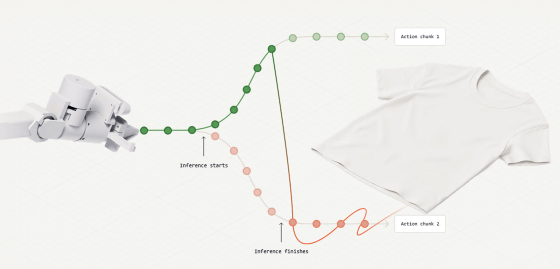
Below is a video recording the process of folding clothes with an AI-equipped robot arm. The AI robot continuously thinks about how to fold the clothes, but while thinking about how to fold them, the shape of the clothes changes due to gravity and the force applied by the robot itself, so it cannot fold them as intended.
In order for an AI-equipped robot to perform accurate and fast operations, it is necessary to take into account 'real-time changes while the AI is thinking.' The research team developed 'real-time chunking (RTC)', an algorithm that can give the AI model the ability to respond to real-time changes, and is designed to update the calculation content based on new information while maintaining a consistent strategy of the AI model.
Below is a video of an AI-equipped robot arm performing the task of 'strike a match, ignite it, and light a candle.' The left side is an AI model that uses RTC, and the right side is a conventional AI model. The AI model that uses RTC was able to perform the task accurately.
For the task of 'inserting a LAN cable,' the AI-equipped robot arm (left) that used RTC was able to execute the task faster.
The AI-equipped robot arm using RTC (left) was able to fold clothes more accurately and quickly than the conventional AI-equipped robot arm (right).

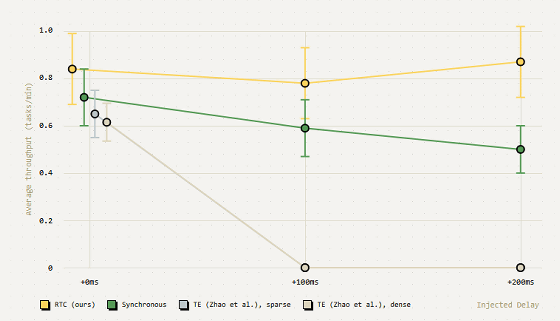
In the graph below, the horizontal axis shows the 'time it takes to calculate an action' and the vertical axis shows the 'number of tasks that can be completed per minute.' The AI-equipped robot arm (yellow) that uses RTC was able to maintain high task execution efficiency even when the time it took to calculate increased.
The research team aims to refine RTC so that it can also handle situations such as 'stopping action to think more deeply.'
Related Posts: