Meta releases AI model 'V-JEPA 2' for creating smart robots, capable of physically correct inference and useful for developing 'robots that think before they act'

Meta has released an AI model called ' V-JEPA 2 ' that is capable of physically correct inference. V-JEPA 2 is trained on videos of real-world events and is said to be useful for developing 'robots that can infer and act on the next event that will occur based on the surrounding situation.'
Introducing V-JEPA 2
Introducing the V-JEPA 2 world model and new benchmarks for physical reasoning
https://ai.meta.com/blog/v-jepa-2-world-model-benchmarks/
Humans can act while intuitively predicting physical events, such as 'walking down a crowded road while avoiding people and obstacles' and 'throwing a ball and predicting where it will land.' Meta's ultimate goal is to realize 'advanced machine intelligence (AMI)' that has the ability to 'understand the physical world and act while predicting the reaction to its own actions,' just like humans. We are developing a 'world model' that can understand, predict, and plan physically correct things in order to realize AMI.
The newly released V-JEPA 2 is an AI model that is positioned as the 'most advanced global model.' Training for V-JEPA 2 was divided into two stages. In the first stage, it was trained using more than one million hours of video footage of real-world events, such as 'picking up the plate when the food is finished,' and successfully gained the ability to infer future situations from the current situation.

In the second stage of training, the robot studied a total of 62 hours of video from the video dataset '
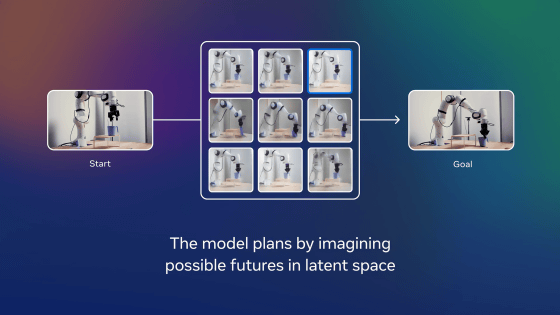
Ultimately, V-JEPA 2 became an AI model with 1.2 billion parameters. V-JEPA 2 took 1/30th the time it took
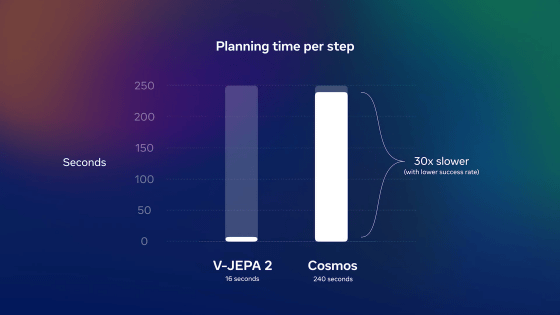
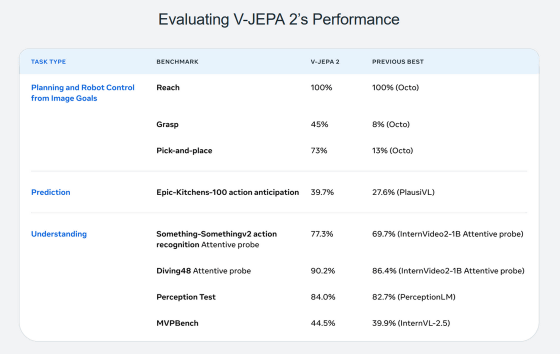
Below is a performance comparison table between V-JEPA 2 and existing models. V-JEPA 2 outperformed existing models in the three areas of 'planning,' 'prediction,' and 'understanding.'
The V-JEPA 2 model data is distributed at the following link.
V-JEPA 2 - a facebook Collection
https://huggingface.co/collections/facebook/v-jepa-2-6841bad8413014e185b497a6
In addition, the code necessary to build V-JEPA 2 is available in the following GitHub repository.
GitHub - facebookresearch/vjepa2: PyTorch code and models for VJEPA2 self-supervised learning from video.
https://github.com/facebookresearch/vjepa2
In addition, Meta has released three benchmarks that can measure how accurately AI models can understand and reason about the physical world. The names and descriptions of the three benchmarks are as follows:
・IntPhys 2
The AI model is fed a pair of videos, one of which has the same content up to a certain point, and the other of which has a physically correct movement and a physically incorrect movement, and the model is asked to determine which video is physically correct. This allows the AI model to evaluate its ability to recognize physically correct movements.
・Minimal Video Pairs (MVPBench)
It assesses AI models' ability to understand physics by presenting multiple choice questions designed to help them avoid shortcuts that rely on superficial cues or biases.
・Causal VQA
It is possible to evaluate a visual language model's 'ability to answer questions about physical causality.'
Although humans can answer the above three benchmarks accurately with an accuracy of 85 to 95 percent, the accuracy rate of existing models, including V-JEPA 2, is overwhelmingly lower than that of humans. Meta aims to develop an AI model that can record high scores in these benchmarks as well.
Related Posts: