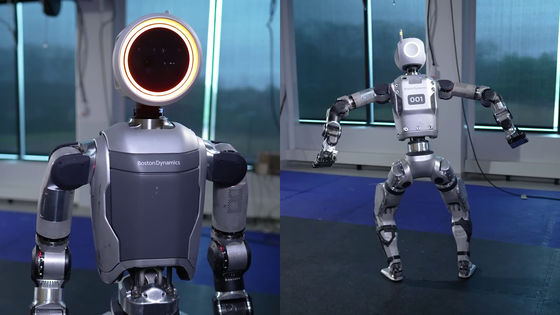
What will enable China to surpass the US and secure an advantage in the robotics industry?

In recent years, the demand for the robotics industry has been increasing, with
America Is Missing The New Labor Economy – Robotics Part 1 – SemiAnalysis
https://semianalysis.com/2025/03/11/america-is-missing-the-new-labor-economy-robotics-part-1/
According to the analysis company SemiAnalysis, China's efforts to domestically produce robots are progressing smoothly, and Chinese manufacturers' share of the domestic robotics industry in China was 30% as of 2020, but is expected to reach 50% by March 2025. In addition, some Chinese manufacturers have left the low-end robot market, which has grown to rival large Western companies, and have begun to enter higher price ranges in recent years.
A prime example is the Unitree G1, developed by Chinese robotics developer Unitree, which SemiAnalysis describes as 'demonstrating the high technological capabilities of Chinese manufacturers that are not reliant on American parts.'

Behind the rapid development of Chinese manufacturers in the robotics industry are the strong driving force of the Chinese government, overwhelming manufacturing capabilities, the characteristics of the domestic market, and strategic investments with an eye to the future. In fact, the Chinese government has positioned the robotics industry as a 'key area of national strategy' and is promoting active investment and subsidy policies through plans such as 'Made in China 2025. ' In particular, in recent years, the government has been making intensive investments in humanoid robots, viewing them as a new engine of economic growth.
China, which has established itself as the world's factory for many years, also has advanced mass production technology and a huge industrial base. This base is also a factor that puts China far ahead of other countries in terms of cost performance and production speed in robot manufacturing. Specifically, if you were to manufacture a Universal Robots ' UR5e ' in the United States, the cost would increase by about 2.2 times compared to manufacturing it in China. Chinese companies also have a high share of the global market for important components such as batteries.
Some Chinese robot manufacturers are working on vertical integration of key components, and in fact, robot manufacturer ESTUN 's in-house production rate has reached 95%, which can significantly improve the speed and flexibility of product development.
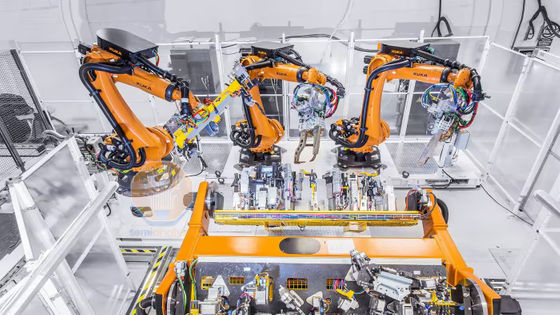
The fiercely competitive Chinese domestic market favors companies that can expand their scale the fastest, and this environment encourages companies to rapidly develop and improve their products. A prime example of this is
In addition, China's robotics industry has a high level of adaptability to changes in the external environment and a strong supply chain. During the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, Chinese manufacturers quickly advanced automation to make up for labor shortages.
Until now, the robotics industry has been dominated by the United States, as exemplified by Boston Dynamics. However, in recent years, that dominance has been lost, and SemiAnalysis points out that 'the American economy has placed emphasis on digital innovation, cutting-edge technology, and the service industry, which has resulted in a decline in manufacturing capabilities. As a result, American manufacturers have been setting up production bases overseas, which offer better cost performance. As a result, the domestic manufacturing base has become poor and there is a lack of manufacturing capacity for parts and materials necessary for robotics.' Furthermore, the principle of 'Made in America' labeling allows major parts imported from China to be labeled as 'Made in America' even if they are assembled in the United States, making the reality of overseas dependence unclear.
In addition, while China is developing its robotics industry through long-term national initiatives, the United States only has systems such as the CHIPS Act, whose direction changes with each administration, and there is no consistent strategy. In addition, it has been pointed out that the 'Big 4' companies that have led the robotics industry for many years, such as FANUC, ABB, Yaskawa Electric , and KUKA, are less willing to invest in research and development and develop next-generation robots than Chinese manufacturers. On the other hand, China's Siasun has acquired a vocational training school in Germany and is actively working to develop human resources and acquire technical know-how overseas.

According to SemiAnalysis, 'general-purpose robotics' that can perform any task in any environment is the 'holy grail' of modern robotics, and the first country to successfully develop it will benefit greatly. Modern robots are limited to structured environments and static tasks, but in recent years, hardware constraints, data shortages, and AI limitations are being overcome.
In the United States, there is a growing awareness of the current situation in which the country is lagging behind in the robotics industry, and there are also calls for cooperation between the government, industry, and research institutes. SemiAnalysis argued that 'in order to prevent China from dominating the robotics industry and for the United States to remain competitive in the future, it is urgent to formulate an appropriate national strategy, restructure domestic manufacturing, strengthen the supply chain, and invest in research and development.'
Related Posts:
in Posted by log1r_ut