Will GPT-4 and Stable Diffusion comply with the EU's proposed AI regulation, which includes restrictions on generative AI?

On June 14, 2023, the European Parliament, the EU's legislative body, overwhelmingly
Do Foundation Model Providers Comply with the Draft EU AI Act?
https://crfm.stanford.edu/2023/06/15/eu-ai-act.html

A bill to regulate AI was submitted to the European Parliament in 2021, but at the time it focused on the use of AI in areas such as self-driving cars, corporate recruitment tests, bank lending, and immigration and border control. However, in recent years, AI has emerged that can generate images and text with such precision that they are indistinguishable from those created by humans, so on June 14, 2023, the EU adopted an amendment to include regulations on generative AI.
The newly adopted EU AI Act includes explicit obligations for providers of foundational models, such as OpenAI and Google. Foundational models are large-scale AI models that employ self-supervised or semi-supervised learning and are trained on vast amounts of data. Well-known examples include OpenAI's GPT-4 and Stability AI's Stable Diffusion v2 . These foundational models can be applied to user-facing AI for a variety of downstream tasks.
Some believe it will be difficult for existing infrastructure models to comply with the EU AI Act. OpenAI CEO Sam Altman stated, 'If we can comply, we will comply. If we can't, we will cease operations. We will try, but there are technical limits to what we can do.' He expressed the view that failure to comply with the regulations would force the company to cease operations in the EU.
CEO Sam Altman says OpenAI will leave the EU if there is serious regulation - GIGAZINE

The EU AI Act will not only regulate AI development companies within the EU, but will also apply to non-EU companies that provide services to people living in the EU, and the fines could be huge. As the world's first AI regulation bill, it will set a precedent for AI regulation bills that will be adopted around the world in the future, and so the EU AI Act is of great significance for technology companies around the world.
The CRFM research team published a report investigating whether various foundation models comply with the EU AI Act. The research team extracted 12 requirements from the EU AI Act that are relevant to foundation model developers, and rated the extent to which existing foundation models comply on a five-point scale from 0 to 4.
The research team identified 12 requirements for the foundation model:
Source of data: Describe the source of the data used for training.
Data governance: Training should be done using data that has been governed by data governance measures (relevance, bias, appropriate mitigation).
Copyrighted Data: Describe any copyrighted data used in training.
Computing: Disclose the computing used for training (model size, computer power, training time).
Energy: Measure your energy expenditure during training and take steps to reduce it.
Capabilities and limitations: Describe capabilities and limitations.
Risks and mitigations: Describe any foreseeable risks and associated mitigations, and if the risks cannot be mitigated, explain why.
Evaluation: To evaluate against public or industry standard benchmarks.
Testing: Reporting internal and external test results.
Machine-Generated Content: Disclose any generated content as being generated by a machine, not a human.
Member State: Disclose the EU Member State in which the market is located.
Downstream documentation: Providing sufficient technical compliance for downstream processes to meet the EU AI Act.
The research team evaluated the following base models: OpenAI's 'GPT-4', Cohere's ' Cohere Command ', Stability AI's 'Stable Diffusion v2', Anthropic's ' Claude ', Google's ' PaLM 2 ', BigScience's ' BLOOM ', Meta's 'LLaMa ', AI21 Labs' ' Jurassic-2 ', Aleph Alpha's ' Luminous ', and EleutherAI's ' GPT-NeoX '. The results are as follows:
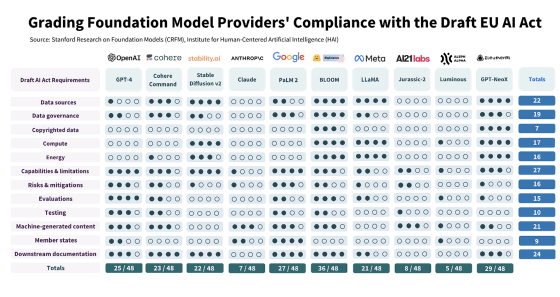
The survey results show that compliance with the EU AI Act varies greatly among companies, with companies such as AI21 Labs, Aleph Alpha, and Anthropic scoring less than 25%, while BigScience achieved a score of over 75%. Additionally, GPT-4 and Stable Diffusion only achieved 25 out of 48 points and 22 points, respectively, which are roughly half of the criteria.
The research team identified several problems with the underlying models they investigated: 'Very few providers disclose their copyright status,' 'They don't report the energy used to develop the models,' 'They don't adequately disclose risks and mitigation measures,' and 'They lack an evaluation standard or audit ecosystem.'
While many foundational model developers are unable to comply with the EU AI Act, the research team hopes that the EU AI Act will bring about significant changes in the foundational model ecosystem, potentially enabling these companies to improve transparency and accountability. 'If foundational model providers take collective action as a result of industry standards and regulations, we believe it should be commercially possible to achieve sufficient transparency to meet data, computing, and other relevant legal requirements,' the research team said, calling on foundational model developers and policymakers to take action.

Related Posts:
in AI, Software, Web Service, Posted by log1h_ik